This excellent interactive tool provides good examples of chi-square thinking and interactions. For more commentary, this write-up of Orth's research is an easy read.
Also, it is an example that doesn't involve politics or COVID. There is a time and place for both in the statistics classroom, but I've missed good, accessible data that doesn't have ANYTHING to do with divisive issues.
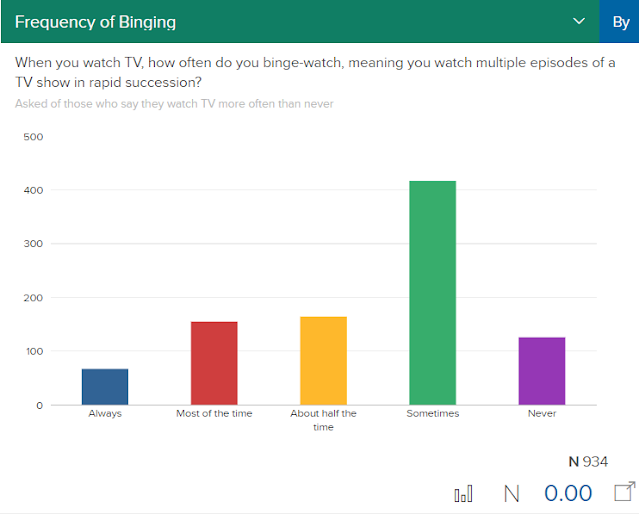
The data is from research that asked people how they watch TV: Streaming services, cable TV, binge-watching, etc. All sorts of information on how we watch TV, and with this easy-to-use website, you can create tables from this data. Tables that help you teach all kinds of ideas.
You can turn chi-square goodness of fit for whether or not people binge their TV.
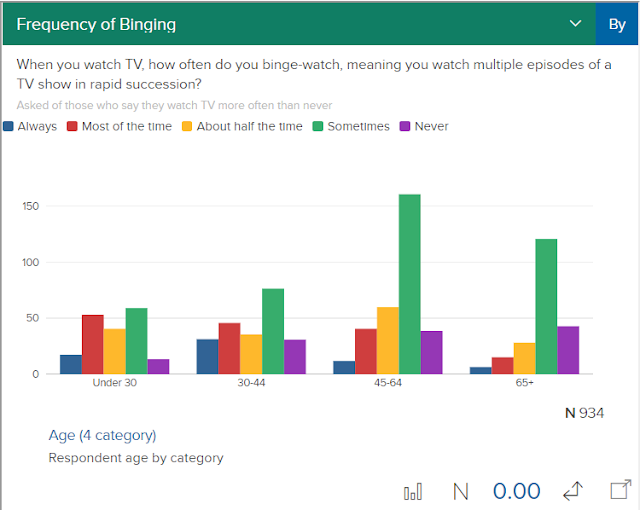
Into a chi-square test of independence by investigating binging by age (categorized).
You can also change the data visualization so you can see the data in a very traditional chi-square table
You can also use these charts to discuss interactions. For example, you can display the data by n-size or by percentage, etc. They aren't super advanced, but I think it is nice to have an example that uses a VERY accessible topic (how we watch TV). Also, I imagine a person could give their students a worksheet of different interactions to graph out via the tool and then describe.


Comments
Post a Comment