This data is now old. And it described global warming, not climate change, which is a crucial language distinction. So you can imagine my delight when Pew recently released updated and improved data investigating this issue.
In my attempt to keep the mood light when discussing an example featuring 1) religion, 2) climate change, and 3) politics, I ask students to think about how many different opinions are probably represented around their family's Thanksgiving table. Despite having much in common as a family, like, perhaps, geography, shared stories, and religion, there are still a lot of within-group differences of opinion.
This leads to a discussion about people of different religions having between and within group differences of opinion regarding beliefs about global climate change.
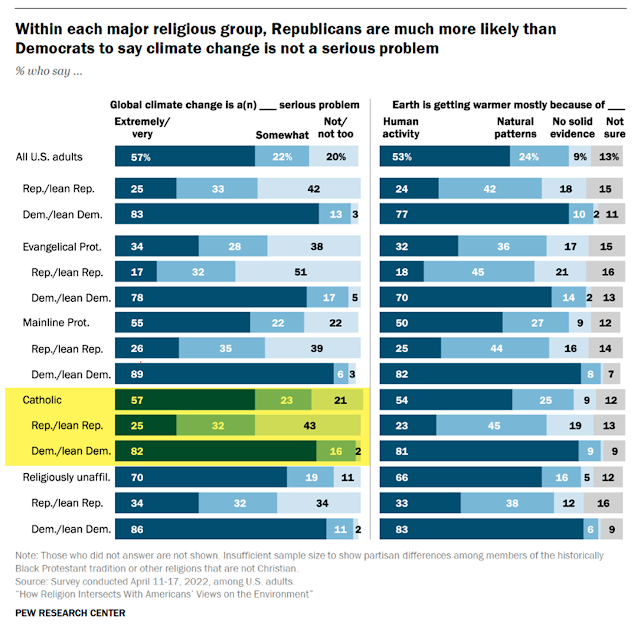
I start by discussing the between-group differences between major American religious groups, like Evangelicals and Catholics (see highlighting).
 |
| https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2022/11/17/how-religion-intersects-with-americans-views-on-the-environment/ |
NOTE: I understand that you wouldn't analyze this data with ANOVA. However, it is helpful to point out that 57% of Catholics think climate change is a severe problem, versus 34% of Evangelicals. This is an example of a difference between groups. Religion, and as IV, is related to the DV (proportions who think climate change is a significant problem).
Then, I describe within-group differences for religious groups. Below, Pew provided data on within-group differences between Democrats and Republicans in the main religious groups.
**NOTE: I realize this isn't the source of all within-group variability within each religion! And I make sure my students do as well**
 |
| https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2022/11/17/how-religion-intersects-with-americans-views-on-the-environment/ |

Comments
Post a Comment