The Pudding took a data-driven approach to test a popular hypothesis: Women's pockets are smaller than men's pockets.
 |
Authors Diehem and Thomas sent research assistants to measure the pockets on men's and women's jeans. They even shared supplemental materials, like the exact form the RAs completed.
 |
| https://pudding.cool/2018/08/pockets/assets/images/MeasurementGuide.pdf |
And they used fancy coding to figure out the exact dimensions of the jeans. Indeed, even when women are allowed pockets (I'm looking at you, dressmakers!), the pockets are still smaller than they are in men's jeans.
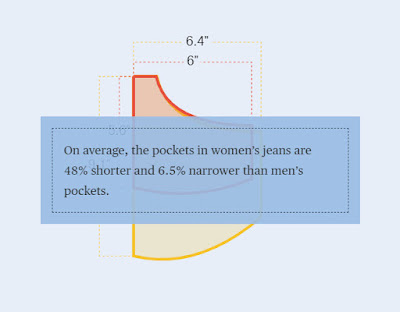 |
They came to the following conclusion:
Amen.
Anyway, there are a few ways you can use this in the classroom:
1) Look at how they had a hypothesis, and they tested that hypothesis. Reasonably, they used multiple versions of the same kind of pants. If you check out their data, you can see all of the data points they collected about each type of jeans. They even provide supplemental materials, like the data collection sheets, their data, and the code they used to figure out the dimension of each pocket. Honestly, that is good science and good transparency.
2) They report the average pocket dimensions, so plenty of means to discuss.
3) They kindly shared their data. With the data they provide, you could conduct an independent t-test, comparing men's jeans and Women's jeans, using any of the pocket dimension measures as a DV.
4) You could also conduct an ANOVA, with jean style as a factor with four levels (boot-cut, skinny, straight, slim), using any of the pocket dimension measures as a DV.


Comments
Post a Comment